PLA vs ABS: What's the difference?
Oct 28,2023 | 3D4Create
What are the differences between PLA and ABS? How do they compare in terms of print settings, flexibility, strength, and toxicity? Understanding the pros and cons of each will help you select the optimal material for your specific 3D printing needs. Read on to find out!
What Are the Optimal Printing Temperatures for PLA and ABS?
PLA prints at lower temperatures, usually between 190°C and 220°C. This makes it ideal for use on basic 3D printers that may not reach higher temps. PLA can also print on unheated print beds, though some heating between 50°C-60°C is recommended to prevent warping.
ABS requires higher hot-end temperatures between 220°C and 250°C. Additionally, ABS printing necessitates a heated print bed between 90°C-110°C to prevent warping and delamination. This limits the use of ABS to higher temperatures which can only be achieved with more advanced presses.
What Heated Bed Temperatures Work Best for PLA vs ABS?
PLA prints well at room temperature without the need for a heated bed. However, using a bed temperature of 45-60°C is recommended to minimize warping. On the other hand, ABS requires a higher heated bed temperature of 90-110°C to prevent severe warping and detachment from the print surface.
How Fast Can You 3D Print with ABS Compared to PLA?
ABS and PLA filaments can be printed at similar speeds, typically around 60 mm/s, allowing the same slicer settings to be used between materials. PLA tends to have more flexibility for faster speeds, with 150 mm/s or greater possible with optimized setups. ABS has a more limited ideal speed range of 40-60 mm/s for quality results.
The exact speed will depend on other factors like nozzle temp, layer height, etc. But in general, PLA can be pushed faster than ABS while maintaining print quality. So print speed is rarely the deciding factor in choosing ABS or PLA for a particular print.

Does ABS Have Better Heat Resistance Than PLA?
When high heat resistance is needed, ABS is better than PLA. ABS has a glass transition temperature of 105°C compared to PLA's 60°C. As PLA approaches 60°C, it can rapidly lose structural stability, causing supported objects to droop and deform. So for applications with exposure to higher temperatures, ABS maintains its integrity better than PLA.

What Is the Shrinkage Rate for PLA and ABS Materials?
PLA tends to have a lower shrinkage rate of around 0.3% as it hardens into its final formed shape. This allows PLA prints to retain more accuracy and precision compared to their digital designs. ABS, on the other hand, displays higher shrinkage ranging from 0.4% to 0.9% after being extruded and cooling into an object. The greater shrinkage rate of ABS can introduce more deviations between the printed product and the original CAD model.
Considering the higher shrinkage helps improve the dimensions of ABS prints. In applications where maintaining exact dimensions is critical, PLA's lower shrinkage makes it preferable over ABS when possible.

Which Has More Flexibility, PLA or ABS Filament?
In terms of flexibility, PLA is generally considered a rigid, brittle plastic while ABS has more flex.
PLA has high stiffness with little ability to bend or distort shape under load. Any bending force applied to a PLA print risks fracturing or snapping the part at that joint. This makes PLA unsuitable for components that need to exhibit any flexion in use.
ABS possesses greater toughness and pliability compared with the more rigid PLA. Thin ABS prints can bend repeatedly without breaking, while thicker prints allow for some flex and distortion from applied loads before permanent deformation. This lends ABS well to functional components seeing force or fatigue.

PLA easily breaks in half under pressure

ABS is not as breakable as PLA (it bends rather than snaps in half)
Is ABS Stronger Than PLA?
Yes, ABS is generally considered to be stronger than PLA when comparing their mechanical properties. ABS is known for its high impact resistance and toughness, making it a popular choice for applications that require durability and resistance to physical stress.
Although ABS is stronger than PLA, it's important to note that strength can vary depending on factors such as the specific brand, composition, and manufacturing process. Additionally, the strength requirements of a particular application should also be considered when choosing between ABS and PLA.
Are PLA and ABS 3D Printing Filaments Toxic?
Printed PLA objects are considered non-toxic and safe. However, printing PLA emits low concentrations of VOCs (volatile organic compounds) as a byproduct, so ventilation is recommended during printing as a precaution.
In contrast, ABS releases significantly higher VOC and nanoparticle emissions during printing, requiring printer enclosures and ducting for proper ventilation. However, once printed, ABS objects themselves are non-toxic with no major health effects. So both plastics are safe after printing, but ABS has greater air quality risks during the printing process itself.
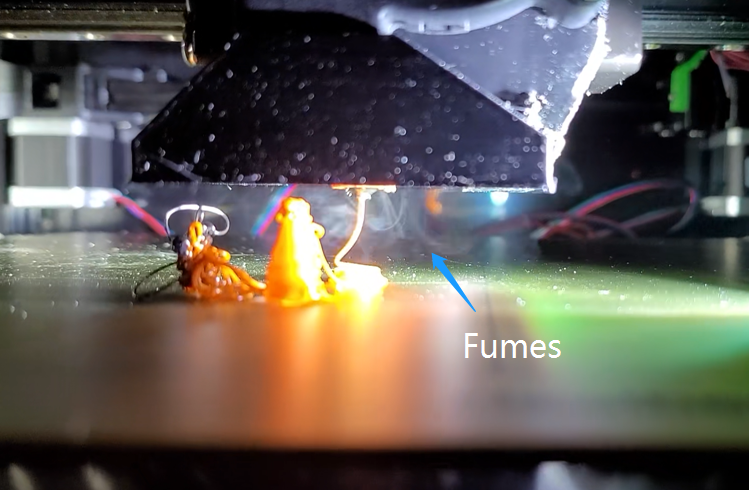
Air quality risk when 3D printing with ABS
Do PLA and ABS Prints Produce Fumes When 3D Printing?
Heated filaments release fumes during printing, with some more pungent than others. PLA emits minimal odor and relatively harmless fumes due to its plant-based nature. But ABS produces significantly more toxic fumes with a very strong unpleasant smell. Opening an enclosure after ABS printing can blast concentrated odors.
Proper ventilation is highly recommended, especially with ABS. Air filters can help reduce exposure to the harmful particulates released. Users should take care when handling enclosures and print in well-ventilated spaces to minimize risks from airborne emissions.

Using an enclosure when printing with ABS safely
Post-processing PLA vs ABS: What Works Best?
Post-processing techniques are used to enhance 3D-printed parts after initial printing. Neither PLA nor ABS have limitations in basic post-processing methods like sanding or painting, although some report that ABS is more easily sanded.
The most popular post-processing for glossy smoothing utilizes solvents. ABS prints can be easily smoothed to a sleek finish with acetone vapor baths. This makes ABS the top choice when solvent vapor smoothing is desired to eliminate layer lines.
If high-quality surface smoothness is essential, SLA 3D printing produces the best surface finish and detail.

ABS is easier to be smoothed with a solvent than PLA (Source: 3D Prototypes and Models)
Comparison of Environmental Stability of PLA and ABS
Unlike ABS, PLA filament has the benefit of being biodegradable. However, the specific high-temperature composting conditions required mean PLA won't fully break down naturally. Industrial facilities are needed for true PLA biodegradation, which can take up to 80 years in regular landfill conditions.
ABS, being non-biodegradable petroleum-based plastic, lasts for centuries before decomposing. So while PLA is marketed as more eco-friendly, real-world biodegradability takes special processing.

Biodegrading process of PLA (photo: 3dbeginners)
What Storage Conditions Do PLA and ABS Filaments Need?
Proper filament storage is important, as some materials are hygroscopic and prone to absorbing ambient moisture. Too much water absorption can create defects like bubbles during printing as the filament is heated. Fortunately, PLA and ABS filaments have low hygroscopic properties compared to other plastics like PETG. Still, sealed air-tight storage is recommended for the longest shelf life.
Drying filament before printing will also help minimize issues from any humidity exposure during storage. Taking steps to keep filament dry preserves the print quality and prevents moisture-related defects.

Is PLA or ABS Easier for Beginners to Use?
For novice makers getting started with 3D printing, PLA has a major ease-of-use benefit over ABS.
PLA sticks well to print beds, resists warping when cooled, and does not require a heated bed. This allows quick printing on almost any type of 3D printer. PLA is very forgiving when dialing in slicer settings as well.
ABS requires more optimized slicing profiles, higher bed temps to increase adhesion, and an enclosed chamber to prevent warping. The extra requirements make ABS more challenging to work with, especially for beginners.
Conclusion
In summary, PLA and ABS have unique advantages for diverse 3D printing applications, as shown in the comparison table.

FAQ
Q1: What is the main advantage of PLA filament?
A1: PLA's main advantages are lower printing temperatures, limited warping, good surface finishes, and overall ease of printing. This makes it good for detailed models and prototypes.
Q2: When should I choose ABS over PLA filament?
A2: Choose ABS for prints needing good mechanical strength, durability, heat resistance, and flexibility. ABS is preferred for functional parts seeing outdoor use or mechanical stresses.
Q3: Can I use PLA on a basic, open-frame 3D printer?
A3: Yes, PLA can be printed on basic, open-frame machines since it does not require a heated bed or fully enclosed chamber. The lower print temps also broaden printer compatibility.
Q4: Is post-processing more difficult with ABS than PLA?
A4: Yes, ABS is more difficult to post-process than PLA. Sanding and painting ABS requires more effort. PLA is easier to modify and finish with post-processing.
Q5: Which is the more beginner friendly material, PLA or ABS?
A5: PLA is generally recommended as the best material for beginners to start with. PLA's ease of printing and lower temperature requirements make it more forgiving.


